At Godrej Consumer Products Limited (GCPL), we maintain a consistent and transparent approach to disclosing both our financial
and non-financial performance, in alignment with established regulatory requirements and global reporting standards. This report,
our sixth Annual and Integrated Report, has been prepared in accordance with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing
Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015, the Companies Act, 2013, and applicable Secretarial Standards. It also
adheres to the International Integrated Reporting (
In addition to fulfilling mandatory disclosure requirements, the report is prepared with reference to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards, following its Sustainability Reporting Guidelines. It is also compliant with the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) framework as prescribed by SEBI. Furthermore, this report aligns with the voluntary reporting requirements under the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI), thereby ensuring that our disclosures meet global benchmarks for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
Our R&D teams lead new product development
across the geographies we operate in

Content of
the report
This Integrated Report aims to offer a holistic overview of GCPL’s financial results and sustainability performance, with the objective of articulating how we create short-, medium-, and long-term value for all stakeholders. The report includes comprehensive insights on:
- Key material issues and the broader operating environment in which we function
- Our corporate governance architecture and oversight mechanisms
- Strategic priorities and execution pathways
- Our approach to value creation across the six capitals
- Performance outcomes mapped against Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- The linkage between material concerns, strategic responses, operational performance, and stakeholder value creation
- Statutory financial disclosures and regulatory compliance reporting
Scope and Boundary
of the report
The scope of this report extends to the full breadth of GCPL’s operations, encompassing our manufacturing facilities and business presence in India, Africa, Indonesia, Latin America, and the United States. Unless explicitly stated otherwise, the information presented is consolidated at the enterprise level to provide a unified view of our operations and performance.
Our reporting approach is aligned with our commitment to transparency, accountability, and responsible business conduct. In line with this, we have adopted the SEBI Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) taxonomy and integrated elements of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework. These standards enable us to offer a detailed, consistent, and investor-relevant view of our sustainability performance, associated risks, and mitigation strategies.
Forward Looking
Statements
This Integrated Report contains forwardlooking statements primarily located in the Management Discussion and Analysis section. These statements reflect GCPL’s strategic objectives and future expectations, expressed through terms such as “may,” “believe,” “outlook,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “continue,” “estimate,” and “expect.” While these projections are grounded in reasonable assumptions and contextual insights, they remain subject to inherent risks, market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and unforeseen external events, which may cause actual outcomes to differ materially from those stated or implied.
These forward-looking statements are reflective of the Company’s perspective as of the reporting date and are not guarantees of future performance. GCPL undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking information, except where mandated by applicable laws or regulatory authorities. Past performance may not be indicative of future results.
Reporting period
The data and narratives presented in this report pertain to the financial year April 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025. To ensure a comprehensive evaluation of our performance, the report also includes comparative data from FY 2023-24 and historical benchmarks from the baseline year of FY 2011–12 (excluding statutory financials). This multi-year approach allows for deeper trend analysis, facilitating a meaningful assessment of our strategic progress, sustainability impact, and value creation trajectory over time.
Double Materiality Assessment
At GCPL, we uphold a strong commitment to people and the planet alongside our pursuit of profit. Our stakeholders include investors, customers, consumers, and communities, expect us to go beyond financial performance and demonstrate broader responsibility.
We conduct a formal materiality assessment every two years or in response to significant changes in the business or regulatory landscape. In 2024, we enhanced our approach by adopting the double materiality framework to better understand which sustainability issues affect our business and how our operations impact stakeholders and the environment. This engagement helped us identify key impacts, risks, and opportunities.
Our assessment focused on identifying and evaluating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues that are relevant to both our business and our stakeholders.
We examined how these material topics align with our business risks, opportunities, and strategic objectives. The goal of the double materiality assessment was to prioritise ESG topics that are most significant to our internal operations and external stakeholder concerns, while recognising the mutual influence between our company and the broader sustainability ecosystem.
The list of material issues identified through the 2024 double materiality assessment has been reviewed and approved by our senior management.
Process flow of double materiality
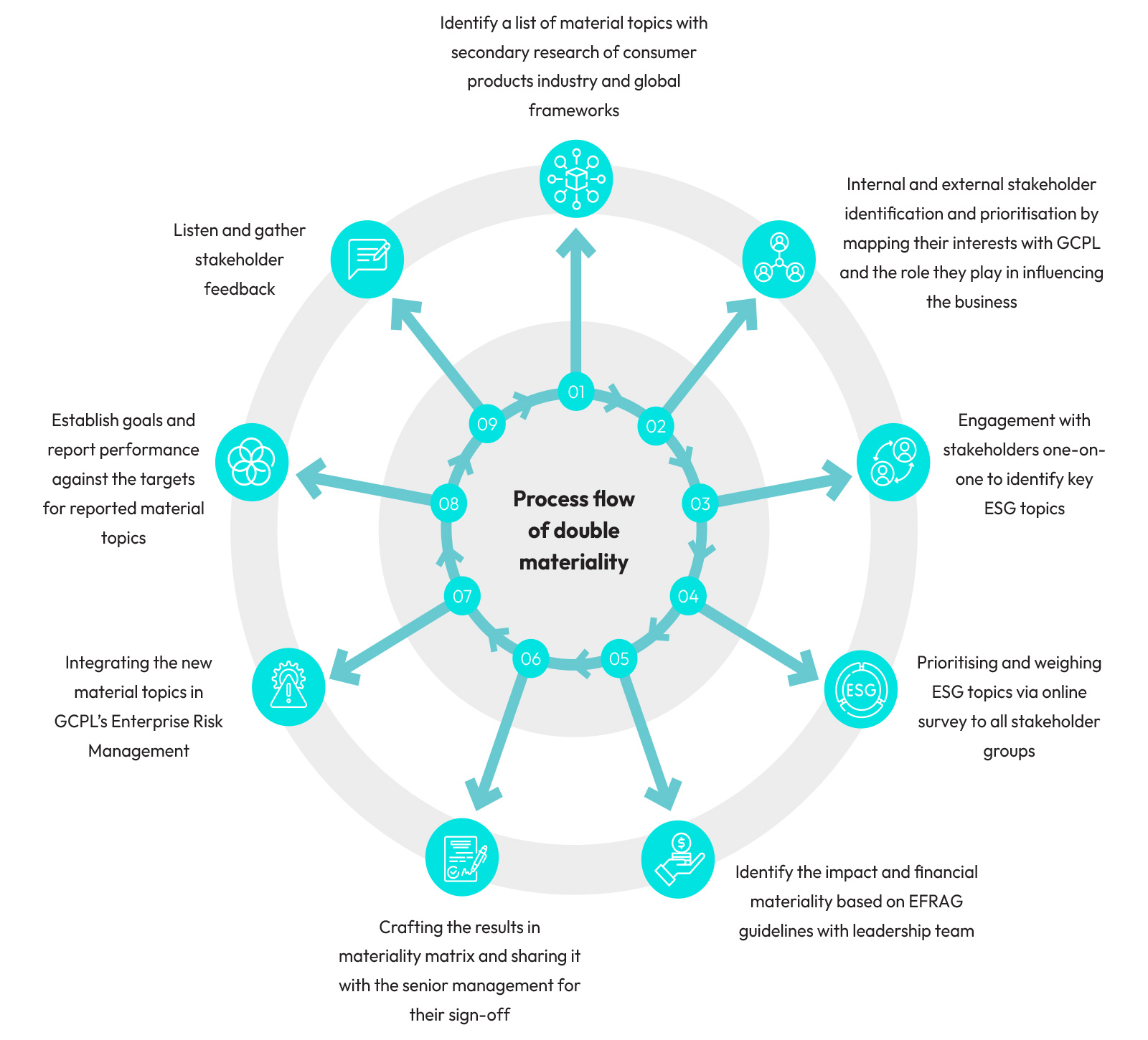
Stakeholder Engagement
To ensure a diverse representation of interests across the regions where GCPL operates, we actively engage stakeholders in our materiality assessment. We are a prominent player in the FMCG sector, and we recognize that our responsibilities go beyond just the consumer goods we provide. GCPL’s success depends on how effectively we manage sustainability factors to create business value and deliver positive outcomes for communities and the environment. Our objective with the double materiality assessment is to pinpoint and prioritise the sustainability factors that have the greatest impact on GCPL, while also acknowledging areas where GCPL can affect results. To achieve this, we initiated engagement with key stakeholder groups to compile a comprehensive list of material issues. Key stakeholders were identified based on their influence, interest, and effect on the business. These included Leadership, Employees, Suppliers, Customers, Investors, NGO Partners, and Industry Associations. We customized our questionnaire for stakeholders to assess their views and priorities.
We evaluated each material issue based on its relative significance among various stakeholder groups, and these findings were consolidated through stakeholder analysis.
Stakeholder Prioritisation
|
Stakeholder |
Stakeholder group |
Ability of a stakeholder to strongly influence GCPL’s performance and operations |
Extent of influence on a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Stakeholders | Leadership Team (L4) | High | High |
| Employees (L3-L1) | Medium | High | |
| External Stakeholders | Suppliers | Medium | Medium |
| Customers | Medium | Medium | |
| Investors | Medium | High | |
| NGO Partners | Low | Medium | |
| Industry Associations | Low | Medium |
Methodology & Findings
For the double materiality assessment for FY 2024–25, we covered GCPL’s operations across both domestic and international markets, including India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Argentina, Chile, Africa, Indonesia, and the USA.
We began by revisiting GCPL’s 2020 materiality assessment and conducted secondary research on global sustainability frameworks and trends within the FMCG sector. This process helped us create a comprehensive list of 40 relevant sustainability topics for evaluation. The preliminary list of topics is outlined below:
Preliminary universe of 40 identified
material topics
-
SrEnvironment
-
1Climate Change
-
2Biodiversity & Land use
-
3Forestation
-
4Ecological Impacts
-
5Energy Management
-
6Emissions
-
7Toxic Emissions
-
8Product Carbon Footprint
-
9Water Management
-
10Waste Management
-
11Environmental Policy & Management Systems
-
12Community Relations
-
13Product Safety & Quality
-
14Labor Practice Indicators
-
SrSocial
-
15Privacy & Data Security
-
16Supply Chain Management
-
17Chemical Safety
-
18Health & safety
-
19Human Capital Development
-
20Materials Sourcing & Efficiency
-
21Customer Relationship Management
-
22Selling Practices & Product Labelling
-
23Product Design & Lifecycle Management
-
24Customer Privacy
-
25Access & Affordability
-
26Talent Attraction & Retention
-
27Sustainable Agricultural Practices
-
SrGovernance
-
28Innovation Management
-
29Business Ethics
-
30Tax Transparency
-
31Ownership & Control
-
32Corporate Governance
-
33Accounting
-
34Competitive Behaviour
-
35Management of the Legal & Regulatory Environment
-
36Critical Incident Risk Management
-
37Systemic Risk Management
-
38Policy Influence
-
39Transparency & Reporting
-
40Macro Economy & Geopolitical Risk
We used the initial list of 40 topics to guide our stakeholder engagement process, which included interactions with employees, suppliers, investors, consumers, industry partners, and NGO partners. A total of 47 one-on-one interviews were conducted both virtually and in person across different geographies. These interviews helped us identify sustainability issues most important to our stakeholders. Based on these insights, we refined the preliminary list to a consolidated set of 20 material topics.
Following this, we conducted an online survey asking stakeholders to rank each topic by its significance. This exercise provided valuable input on perceived and emerging sustainability risks and opportunities. We received 184 responses across all stakeholder groups. Using these responses and applying appropriate weightages to each stakeholder group, we evaluated and prioritised the top 20 topics based on stakeholder preferences.
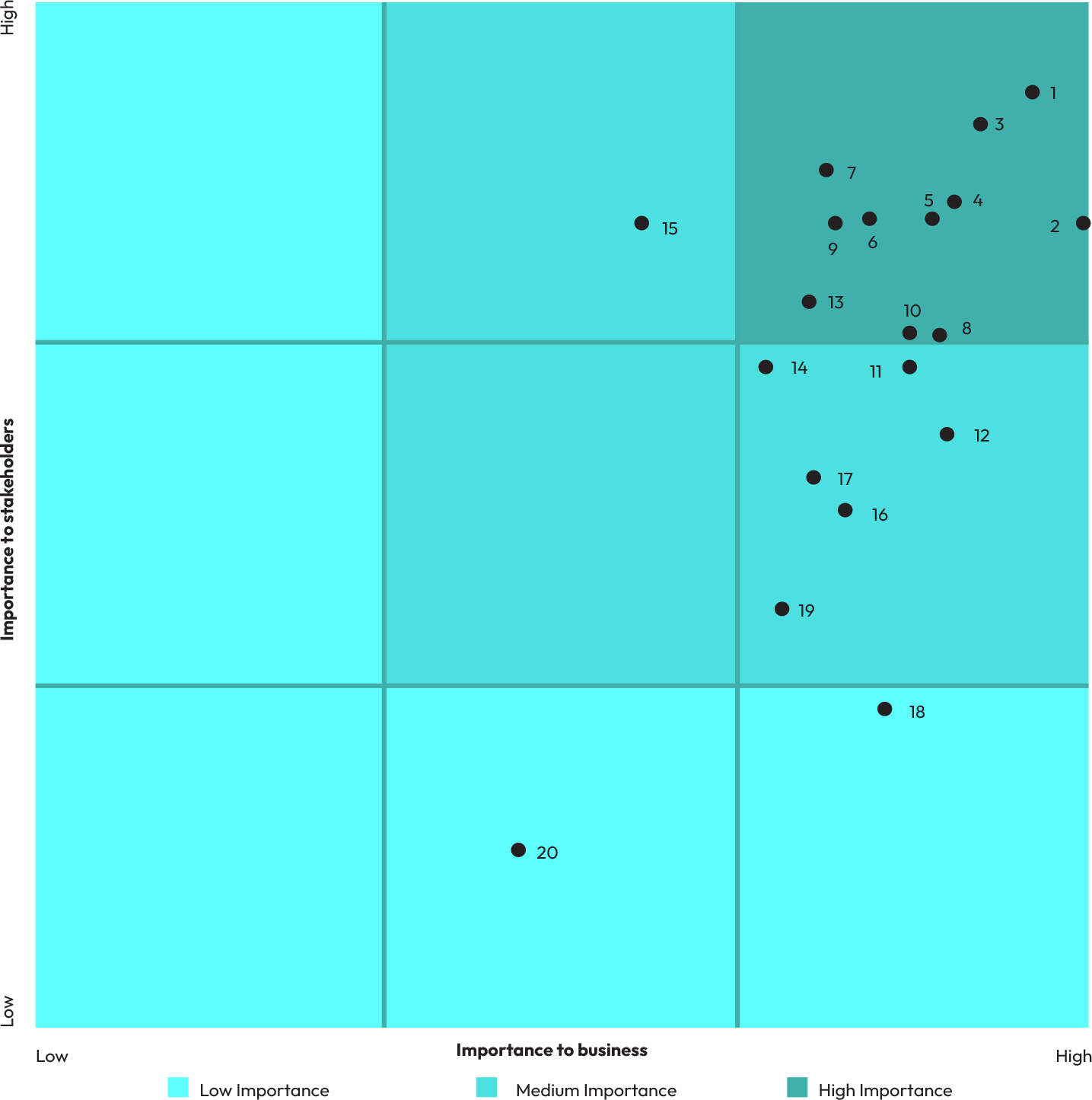
Final list of 20 material topics
|
Rank |
ESG indicator |
Material topics |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S | Occupational Health & Safety |
| 2 | E | Product Safety and Quality Testing |
| 3 | G | Business Ethics and Ethical Marketing |
| 4 | G | Governance and Accountability |
| 5 | G | Research & Development |
| 6 | E | Sustainable Packaging |
| 7 | E | Sustainable Supply Chain Management |
| 8 | E | Renewable Energy |
| 9 | E | Sustainable and Greener Products |
| 10 | S | Diversity & Inclusion |
| 11 | S | Human Capital Development |
| 12 | G | Changing Legal Landscape |
| 13 | S | Product Awareness |
| 14 | G | Demographic Risks |
| 15 | S | Consumer Awareness |
| 16 | E | Carbon Emissionss |
| 17 | S | Community Relationships |
| 18 | E | Water Conservation |
| 19 | S | Talent Attraction & Retention |
| 20 | E | Climate Change |
Double Materiality Assessment
After completing the evaluation, we developed GCPL’s double materiality matrix by plotting each subtopic across two axes: impact materiality and financial materiality.
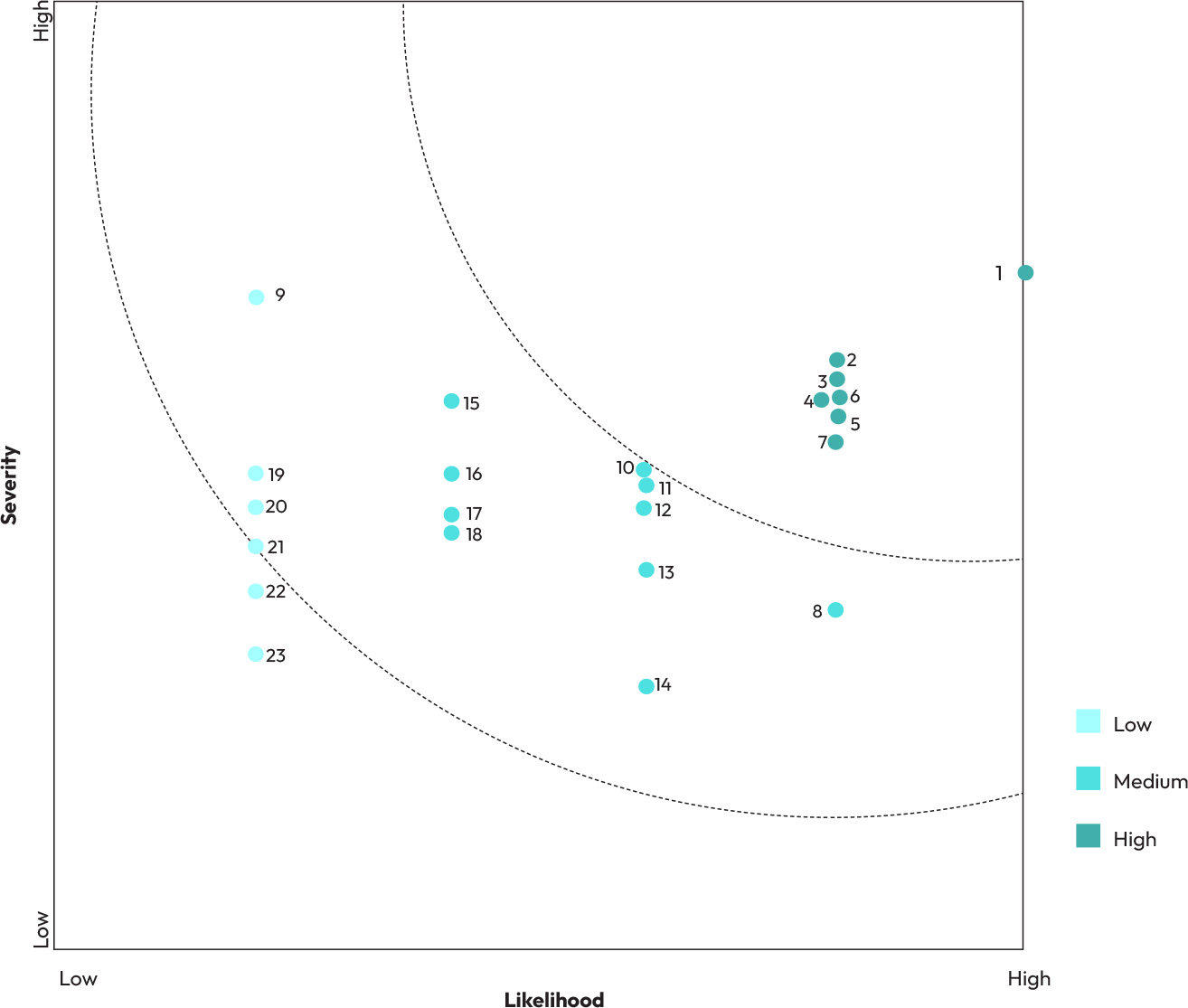
Results of impact materiality assessment
|
Rank |
Material topics |
|---|---|
| 1 | PCR Regulatory Mandates |
| 2 | Increasing Access of Affordable and Greener Products |
| 3 | Alternative Material for Tin and Aluminium Cans / Overall Reduction in Aluminium Usage |
| 4 | Collection of Post Consumer Plastic Waste |
| 5 | Palm Oil Sourcing |
| 6 | ESG Monitoring and Performance Management of Suppliers |
| 7 | Integration with Renewable Energy |
| 8 | Transparency in Information Disclosure |
| 9 | End-of-Life Recycling of Hair Extension products |
| 10 | Product Innovation |
| 11 | Plastic Packaging Intensity |
| 12 | Infrastructure and Policy in Emerging Markets |
| 13 | ESG Rating for Vendor Onboarding |
| 14 | Women in Senior Leadership |
| 15 | Emerging Regulatory Risk on Product Chemical Safety |
| 16 | Country-wise Product Marketing and Communication Strategy |
| 17 | Product Labeling and Greenwashing |
| 18 | Inclusion of Specially Abled People |
| 19 | Code of Conduct |
| 20 | SOP of Internal Quality Standards |
| 21 | Women Safety |
| 22 | Health and Safety Training |
| 23 | H&S of Value Chain Partners |
subtopics, this matrix was created at both the topic and subtopic levels to highlight GCPL’s key sustainability priorities.
Financial impact materiality matrix

Change in material topics
-
2020
-
Sustainable Packaging
-
Research & Development
-
Responsible Marketing and Communication
-
Building Inclusive and Prosperous Communities
-
Governance and Accountability
-
Occupational Health and Safety
-
Skill Development and Training
-
2024
-
Occupational Health & Safety
-
Product Safety and Quality Testing
-
Business Ethics and Ethical Marketing
-
Governance and Accountability
-
Sustainable Packaging
-
Sustainable Supply Chain Management
-
Renewable Energy
-
Research & Development
-
Sustainable and Greener Product
-
Diversity & Inclusion
*Note: The Double Materiality Assessment was carried out in FY 2024 and will be undertaken again next year as part of our periodic review of materiality, which is conducted once every 2 years.
Top material issues
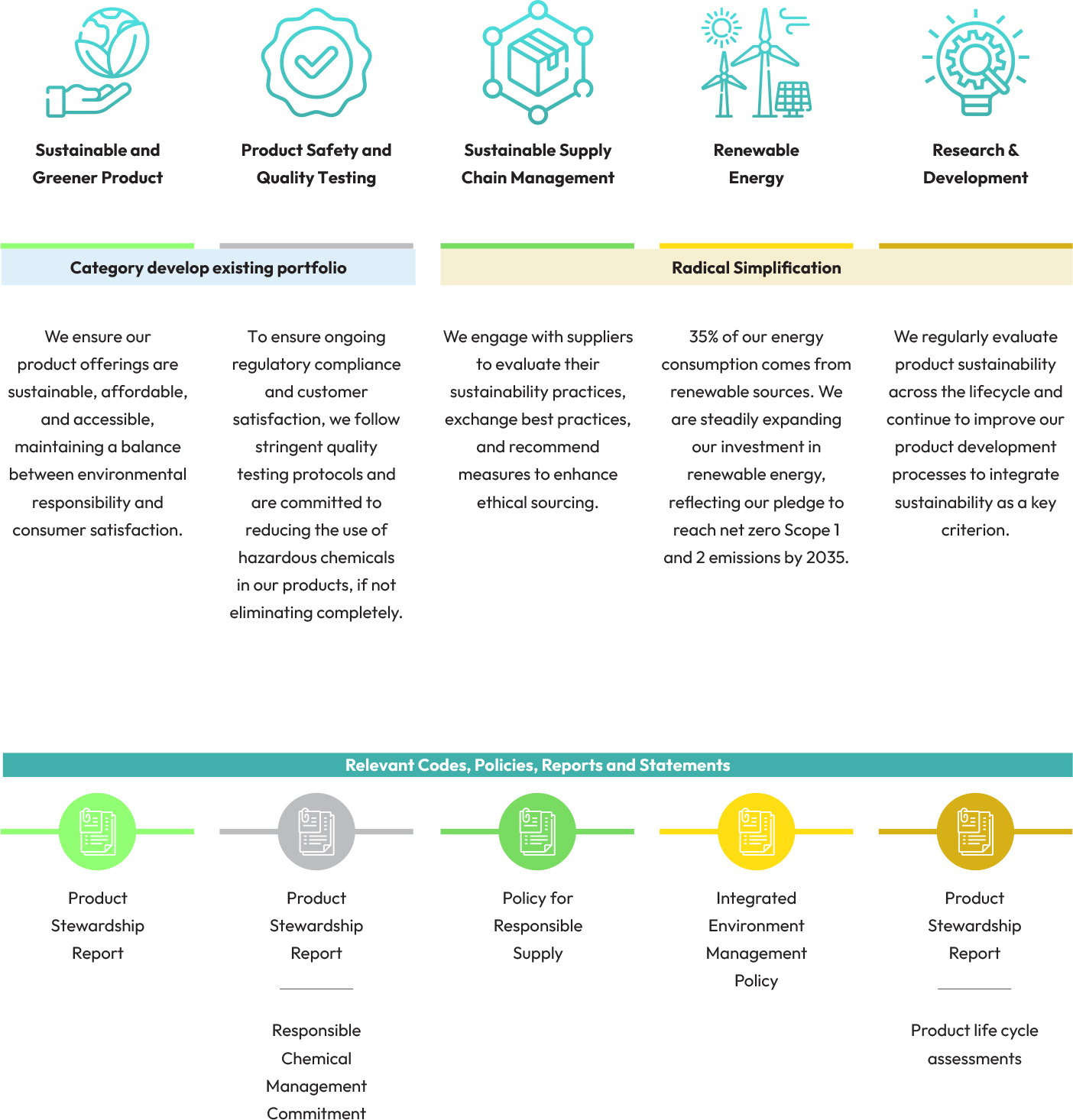
Priority material issues for value creation
|
Material Issue |

Occupational Health and Safety |
|---|---|
| Boundary | Within and outside GCPL |
| Business Case | Ensuring health and safety remains a critical focus at GCPL, particularly due to the physical risks faced by personnel in manufacturing and distribution roles. These factors elevate the chances of workplace incidents. Insufficient training in Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) not only puts employees at risk but also exposes the company to a range of secondary consequences, including legal costs, operational disruptions, increased stakeholder scrutiny, lower employee morale, and damage to corporate reputation. |
| Impact | Risk |
| Relevant Stakeholders | Employees, workers, contractor workers and local community |
| Business Strategy/ Initiative |
To mitigate these risks, we have established a comprehensive Health & Safety policy, supported by welldefined Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and a structured governance framework. This ensures all
incidents are thoroughly investigated and addressed to prevent recurrence. Safety procedures are reviewed
periodically, and both the Central Safety Committee and plant-level committees conduct monthly reviews of
occupational health and safety data. We are proud of our sustained record of zero fatalities across offices and manufacturing facilities, which has contributed to strong employee morale and trust. |
| Target |
By 2026-27, we aim to have–
|
| Progress as of FY25 |
|
| Link to executive compensation | At GCPL, 15% of executive compensation is directly linked to People & Planet goals, aligning with our broader mission to foster an inclusive workplace and support a more sustainable world. Specifically, health and safety targets tied to executive pay include the rollout of a human rights action plan with a focus on safety, reducing the frequency of workplace accidents, and ensuring no fatal incidents occur. |
|
Material Issue |

Sustainable Packaging |
|---|---|
| Boundary | Within and outside GCPL |
| Business Case | The tightening of regulations around plastic use, waste generation & disposal, particularly in regions like India and Africa, could lead to increased short-term compliance costs. |
| Impact | Cost |
| Relevant Stakeholders | Investors, Employees, Customersy |
| Business Strategy/ Initiative | Given that plastic packaging is a key component of most GCPL products, we are actively working to reduce our plastic packaging intensity, defined as the ratio of packaging weight to total product weight. Since the FY2019-20 baseline, we have achieved a reduction of over 20% in plastic intensity, resulting in cost savings and lower Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) obligations. |
| Target |
By 2027, we aim to –
|
| Progress as of FY25 |
|
| Link to executive compensation | At GCPL, 15% of executive compensation is tied to the achievement of People & Planet goals, reflecting our commitment to an equitable and sustainable future. In terms of sustainable packaging, these goals include improving the quality of plastics used, minimizing plastic consumption, and increasing the use of recycled materials in place of virgin plastic. |
|
Material Issue |
Renewable Energy |
|---|---|
| Boundary | Within GCPL |
| Business Case | Transitioning to renewable energy sources not only helps lower GCPL’s emissions but also delivers substantial long-term cost benefits. |
| Impact | Revenue |
| Relevant Stakeholders | Investors, and Employees, |
| Business Strategy/ Initiative | As of now, 35% of GCPL’s total energy consumption is derived from renewable sources, including briquettefired boilers, microturbines for steam generation, co-generation systems, rooftop solar PV, and open access green power wherever available. |
| Target | We had set a target to increase the share of renewable energy in our overall energy mix to 35% by FY2025 |
| Progress as of FY25 | 35% of GCPL’s energy is from renewable sources which achieves our 2025 target |
| Link to executive compensation | At GCPL, 15% of all leaders’ executive compensation is tied to the attainment of People & Planet goals, reflecting our commitment to building a sustainable and inclusive future. Regarding renewable energy, these performance-linked goals include increasing the share of renewables in our energy mix, reducing specific energy consumption, and lowering overall emissions. |
Our R&D teams focus on new product
development that have lower environmental

Material Issues and Materiality Metrics for External Stakeholders

|
|
|---|---|
|
Material Issue for External stakeholders |
Carbon emissions and climate change impact |
| Cause of impact | Operations and our products |
| External Stakeholder(s)/ Impact Area(s) Evaluated | Environment and Society |
| Type of impact | Both positive and negative impact |
| Relevance for external stakeholder(s |
The year 2024 was the warmest on record since 1880, resulting in above-average temperatures and
extreme rainfall across several regions where we operate. These climate events damaged crops and
contributed to rising food prices. Climate change continues to disproportionately impact populations in
emerging markets, many of which fall within our operational footprint.
To address our environmental impact, we follow a proactive three-pronged strategy to reduce carbon
emissions:
|
| Output metrics | % of GHG emissions reduction - We are committed to reducing our GHG emissions intensity by 45% by FY2026, using FY2011 as the baseline. As of FY2025, we have already achieved a 47% reduction. |
| Impact valuation | We assess the environmental impact of our operations and products by applying an internal carbon price of $10 per tCO2 e emitted/reduced, based on shadow pricing to evaluate the environmental value lost/ gained. This pricing covers all three GHG scopes and is applied across all manufacturing-related business decision-making processes, with the objective of minimizing emission impact. |
| Impact metric | In FY2025, we reduced our global Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 12,621 tCO2 e compared to FY2024, equating to an estimated environmental value gain of $126,210. |

|
|
|---|---|
|
Material Issue for External stakeholders |
Water consumption in water-stressed areas |
| Cause of impact | Operations and our products |
| External Stakeholder(s)/ Impact Area(s) Evaluated | Environment and Society |
| Type of impact | Both positive and negative impact |
| Relevance for external stakeholder(s) |
Nearly half of the global population faces severe water scarcity for at least part of the year. Unsustainable
industrial water use can jeopardize local community access to this essential resource. This issue is especially
material to GCPL due to the significant water stress in many of our operational geographies and the critical
reliance of both our business and stakeholders on water availability. At GCPL, we are actively working to reduce our water footprint, both within our operations and across the lifecycle of our products. We conduct regular water assessments at our facilities and in the communities where we operate, implementing targeted initiatives to protect shared water resources. |
| Output metrics | % of water intensity reduction - We are targeting a 40% reduction in water intensity by FY2026 compared to our FY2011 baseline. As of FY2025, we have achieved a 30% reduction. |
| Impact valuation | To measure the environmental impact of our operations and products, we use an internal water pricing mechanism based on a risk-adjusted pricing model to quantify the environmental value lost or gained. |
| Impact metric | In FY2025, we increased our global water consumption by about 26,000 kilolitres compared to FY2024, translating into an environmental value lost of about $9,000 for the communities we serve. |
We actively engage with our stakeholders and incorporate their feedback into our decision
making. Below is an overview of our stakeholder engagement approach and the key steps we
follow to understand the expectations and priorities of each stakeholder group.
|
Stakeholder group |

Leadership Team |

Employees |

Suppliers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whether identified as Vulnerable & Marginalized Group | No | No | No |
| Frequency and manner of stakeholder engagement |
|
|
|
| Sustainability and other concerns |
|
|
|
| Our engagement approach |
|
|
|
|
Stakeholder group |

Customers |

Investors |

NGO Partners |

Industry Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whether identified as Vulnerable & Marginalized Group | No | No | No | No |
| Frequency and manner of stakeholder engagement |
|
|
|
|
| Sustainability and other concerns |
|
|
|
|
| Our engagement approach |
|
|
|
|